Of course, we’re aware of CBD and THC’s abilities. Their medicinal advantages are continuing to be uncovered through research. We’ve recognized for quite some time that CBD is a viable seizure treatment. We also understand that the two chemicals function in different ways from one another.
However, one thing that isn’t frequently discussed is where CBD and THC originate in the cannabis plant. Perhaps you consider this question on a regular basis. Maybe you’ve never given it any thought before. No matter how you look at it, this article will address your questions about these chemicals.
Where Is CBD Found – And What Is It?
CBD, also known as cannabidiol, is one of approximately 100 different cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. While CBD does not produce the mind-altering high that THC does, it may have some psychotropic effects. Some claim that CBD has psychoactive properties and result from its mood-boosting capabilities.
CBD, unlike its close cousin THC, does not cause a high. It has the ability to affect our bodies in beneficial ways without producing the same effects as marijuana use. As a result, it’s especially useful for people who have medical issues but also wish to go about their daily lives effectively.
CBD, unlike THC, has no direct interaction with cannabinoid receptors throughout the body; instead, it is a receptor antagonist.
CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors are the main ones in humans. These help to maintain bodily balance and may aid with functions such as sleep, mood, immune activity, inflammation, pain management, and a variety of other illnesses.
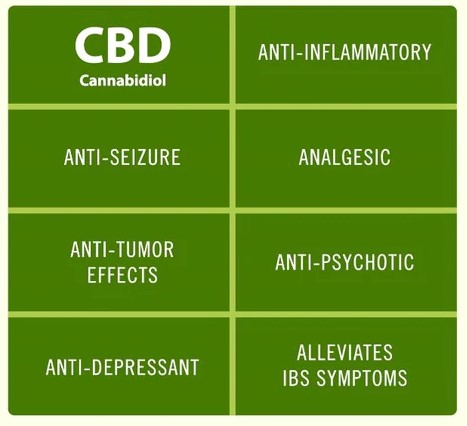
Cannabidiol (CBD) appears to function primarily via CB2 receptors. It has been proven to help with seizure/epilepsy treatment, and it is even FDA-approved for two uncommon epileptic syndromes. CBD also seems to have therapeutic effects on depression, chronic pain, inflammation, anxiety, sleeplessness, MS, arthritis, and a variety of other ailments and health issues.
What About THC?

THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the psychoactive “opposite” of CBD. It causes cannabis’ euphoric effect. THC is a cannabinoid receptor agonist, unlike cannabidiol. This implies it binds to the receptors in a lock-and-key manner, similar to other cannabinoids.
CB1 receptors in the brain and spinal cord are primarily targeted by THC. It has a variety of advantages, including assisting with pains, discomfort, arthritis, inflammation, sleeplessness, nausea, chronic tiredness, hunger loss, depression, chronic stress , and other ailments.
THC, on the other hand, is more popular than ever. While it isn’t for everyone, THC still has a large following, particularly among those who like being high and in an altered state of mind. As a result, THC is frequently used recreationally rather than just medically.
Misconceptions about Hemp, Marijuana, and Where THC and CBD are Found
Many individuals think that hemp is the male version of marijuana, and that CBD only occurs in these males. This is untrue on many fronts.
Hemp is not the “male” form of cannabis, as some may believe. Hemp is a distinct genetic cultivar of cannabis just like any other strain, although it can be male or female. All cannabis strains belong to the same genus and species, Cannabis sativa L., despite popular belief.
Hemp is also chemically distinct from marijuana on several essential levels. First, it has a low THC content, with an average of less than 0.3% by dry weight. Hemp is also phenotypically unique in the sense that its fibrous stem grows higher than marijuana and has fewer blooming buds.
THC and CBD are found in different types of cannabis in multiple areas, but they’re mostly concentrated in the flowers. Let’s have a look at them one by one. THC and CBD are present throughout the plant’s aerial portions, though they’re generally most concentrated in the blooms. Let’s have a closer look.
Where Is CBD Found?
CBD may be found in almost all strains of cannabis, even those with only trace amounts. This includes both cannabis sativa and indica strains as well as hemp. CBD is present in the aerial parts of hemp but not in the roots or seeds. The flowers, stems, and leaves are the aerial parts of the hemp plant, which are located above the soil line.
There are many different ways to extract CBD from the raw cannabis plant material. The most frequently utilized extraction processes are solvent-based. This involves using solvents such as butane, propane, and ethanol (among other things) to extract CBD from the plant material.
The Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) process, which employs carbon dioxide (CO2), is a more advanced solventless extraction technique. The CO2 is frozen and compressed in a special extraction machine until it reaches a supercritical cold liquid state. This fluid then passes through the plant material, removing the cannabinoids and terpenes from it.
There are generally three types of CBD oil for sale on the market today.
- Full-Spectrum CBD Oil: It also includes the full chemical profile of the plant material in its raw form. Cannabinoids, including THC and CBD, as well as terpenes, flavonoids, fatty acids, and other plant components are all present.
- Broad-Spectrum CBD Oil: The cannabis plant material is typically decarboxylated to produce a tincture. This includes a wide range of chemicals from the source plant material. THC, on the other hand, is generally completely removed from the oil.
- CBD Isolate: This is a CBD oil that only contains the phytocannabinoid CBD (cannabidiol) alone. The remaining components of the oil are removed.
Where Is THC Found?
Cannabis sativa and cannabis indica plants produce more resinous trichomes than hemp. THC is contained in trichomes, which are small hairs that grow on the surface of the plant. As stated earlier, hemp contains THC in significant amounts (0.3 percent or less), however cannabis sativa and cannabis indica plants produces higher quantities of resinous trichomes (up to 10%).
THC is present in all of the aerial parts (i.e., the sugar and fan leaves) of a marijuana plant, but it is most abundantly found in the flowers of female marijuana plants. These flowers, which we learned about previously, are covered in tiny resin glands known as trichomes.
What Are Trichomes?
Trichomes are Greek in origin and derive their name from the term ‘Trichōma,’ which means “hair growth.” When viewed through a magnifying glass, they appear to be tiny hairs. Trichomes develop on a cannabis plant when it reaches the flowering stage of its development cycle. They act as a defensive barrier for the plant and serve as an insect repellent.
Trichomes, on average, have a greater cannabinoid, terpene, and flavonoid content than any other portion of the cannabis plant.
The trichomes start the process, and these cells become the source of numerous cannabinoids that marijuana produces.
Trichomes are a form of crystal that can be found in cannabis plants. There are two distinct types of trichomes: glandular and non-glandular trichomes. Cystoliths are another name for non-glandular trichomes.
Furthermore, there are three distinct types of glandular trichomes on a marijuana plant:
- Bulbous: The bottom layer, known as the first layer or lowest layer, contains 1-5% THC and CBD. These are the smallest of the three types, ranging from 10 to 15 microns in diameter and being undetectable to the naked eye. While bulbous trichomes do include cannabinoids and other compounds, their minute size restricts them.
- Capitate-sessile: The hairs are usually longer, thicker, and darker than those on the leaves. They’re called “acicular trichomes” when they have a long, thin stalk and head and appear to be more cannabinoid-rich than bulbous trichomes. These trichomes are generally only visible under a microscope.
- Capitate-stalked: The biggest of the three types of trichomes, ranging in size from 50 to 100 micrometers, are capsulated-stalked trichomes. Capitate-stalked trichomes are visible to the naked eye and can be found on a marijuana plant’s blooms. They have a large gland head that houses cannabinoids and other chemicals, as well as a prominent stalk.
Final Thoughts
There’s no doubt that the medical advantages of CBD and THC are being investigated further all the time. Hopefully, this post has shed light on where these phytocannabinoids can be found in cannabis plants from different species.
The popularity of CBD oil and CBD-based goods has increased dramatically in recent years. Many people have sought out information regarding these chemicals and their effects, as well as a deeper knowledge of them.
Aside from asking consumers about the products’ ability to deliver health advantages, additional fundamental inquiries are asked. THC is typically present in greater amounts in cannabis sativa and indica varieties than it is in industrial hemp. THC and CBD are both present in cannabis leaves, not roots or seeds.
Hemp does, however, have THC in small amounts. THC is present in hemp in only minimal quantities, about 0.3 percent or less. THC is plentiful on the flowers of female marijuana plants’ resin-coated trichomes, where it is known as a cannabinoid profile.
